Digital tools have the potential to revolutionize modern agriculture through precise nutrient management practices that improve fertilizer-use efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint of farming without compromising yield. Reeta Pal, a woman farmer from Uttar Pradesh, is a perfect example of how digital tools can significantly impact livelihood. The additional income from using field-specific recommendations helped improve her family’s livelihood standards and offered opportunities to purchase quality inputs for farm operations.
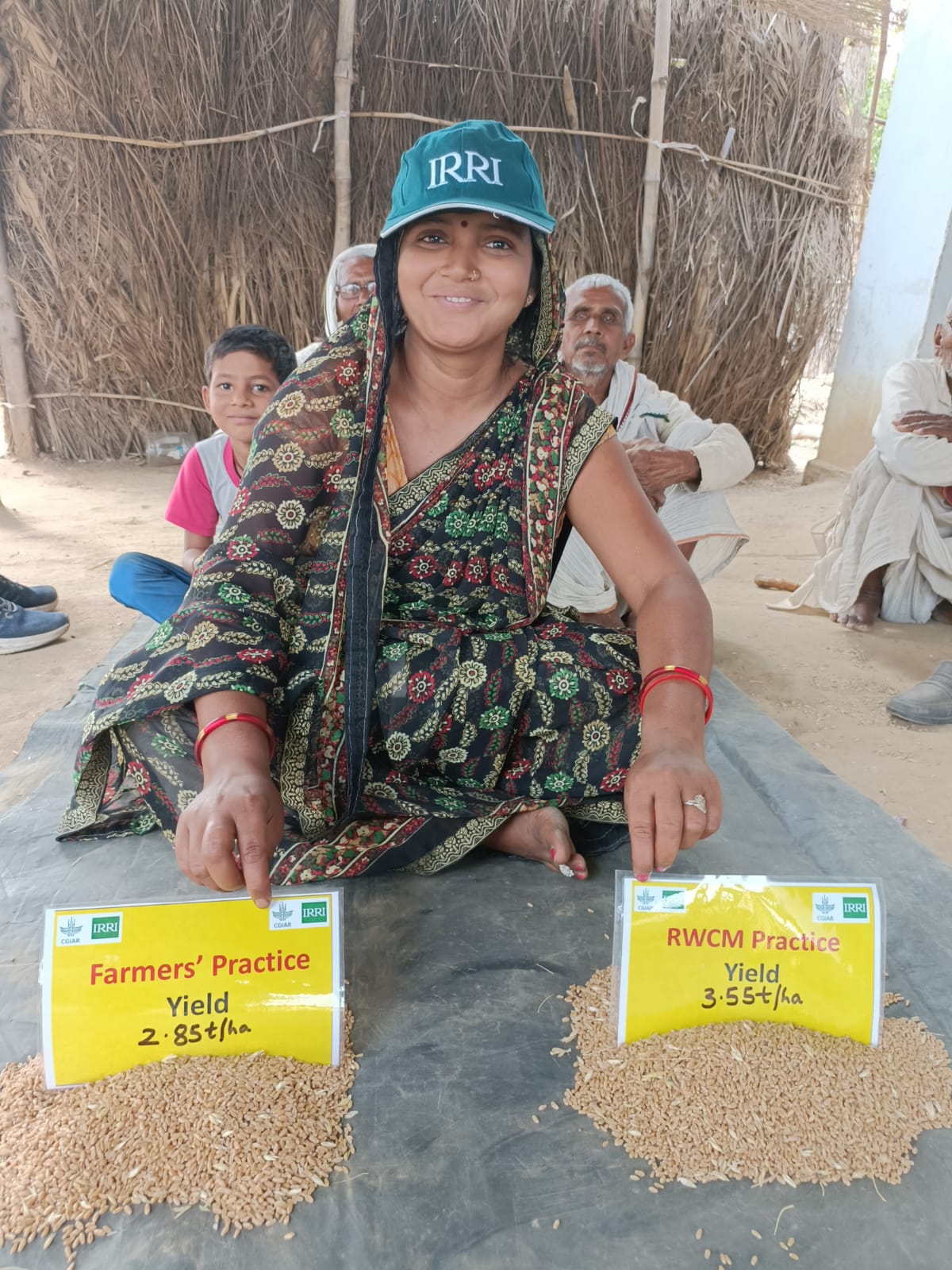

Reeta Pal shows the difference in rice yields between farmer’s fertilizer practices and field-specific fertilizer recommendations generated by a digital tool. (Photo: ISARC)
.
Digital tools have the potential to revolutionize modern agriculture through precise nutrient management practices that improve fertilizer-use efficiency and reduce the environmental footprint of farming without compromising yield.
On the other hand, the lack of awareness of these digital tools can lead to inefficient use of resources, lower crop yields, and environmental pollution. It is crucial to understand the factors that drive farmers’ mindset in adopting sustainable agriculture practices to expand the use of digital tools.
The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) South Asia Regional Centre (ISARC) is developing various digital tools for small and marginal farmers in Eastern Uttar Pradesh.
The Rice-Wheat Crop Manager (RWCM) is a digital web-based decision support tool developed by IRRI to provide field-specific recommendations based on the 4R nutrient management principle (the right source, time, amount, and place) through printed and text message recommendations.
A tool for improving livelihood
Reeta Pal is a woman farmer from Majhiar Village in Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh and her journey is a perfect example of how digital tools can significantly impact livelihood. Ms. Pal participated in the RWCM hands-on training and implemented recommendations.
Before this, she used the conventional farmer’s fertilizer practice (FFP) application method. However, with RWCM, she could tailor her fertilizer usage to the specific needs of her crops.
By following RWCM recommendations, Ms. Pal optimized the application of Diammonium Phosphate and urea while balancing Muriate of Potash and Zinc fertilizer application. This not only improved nutrient-use efficiency and the use of resources but also improved crop yields.
Using RWCM proved to be highly beneficial in reducing fertilizer costs while simultaneously optimizing crop growth and yield. By following the RWCM recommendations, she gained 20% and 24.6% higher grain yield in rice and wheat, respectively, compared to FFP (See Fig. 2). Ms. Pal also observed reduced lodging incidence.
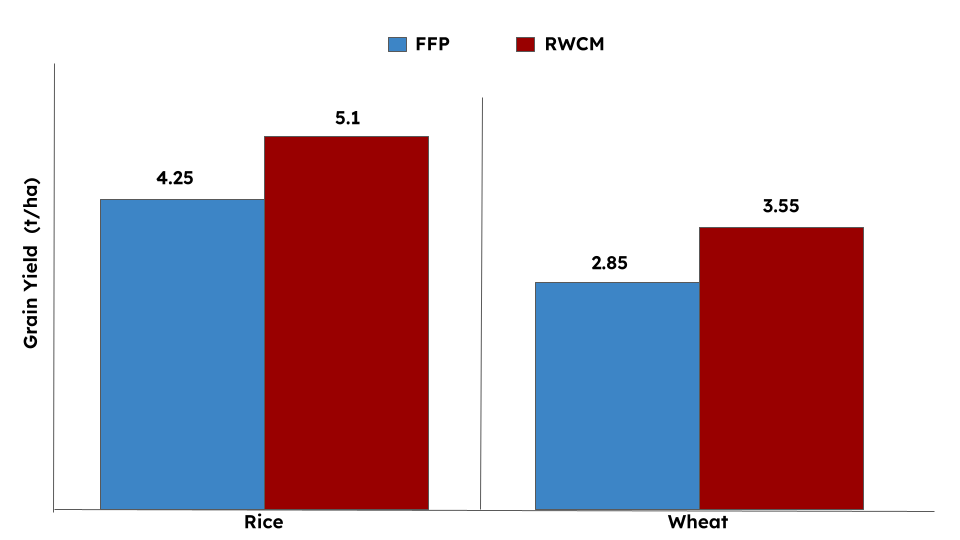
Fig. 2 Grain yield of rice and wheat crop under FFP and RWCM
The additional income from using RWCM recommendations helped improve her family’s livelihood standards and offered opportunities to purchase quality inputs for farm operations.
A woman leading women
Having gained extensive knowledge and experience using RWCM on her own farm, Ms. Pal has taken it upon herself to share this valuable information with other farmers. A member of a Farmer Producer Organization, she encouraged other members of her FPO to opt for RWCM. She initiated training for them and helped them generate RWCM recommendations for their use.
By replicating her success and encouraging fellow farmers to adopt RWCM, she has been able to promote sustainable and efficient agricultural practices in her village.
The sharing of knowledge and resources among farmers is a critical aspect of sustainable agriculture. By collaborating and implementing innovative digital solutions like RWCM, farmers can reduce their yield gaps and attain high returns to improve their livelihood.
Digital innovations for food security
The dissemination and scaling of digital innovations can bring about a significant change in day-to-day agronomic management and improve soil and ecosystem health.
It is, therefore, essential for public-private sector partners, extension agents, and other stakeholders to develop synergies to ensure that these tools are made accessible and affordable to farmers worldwide.
That strategy will enable them to harness the full potential of digital innovations for food security, sustainable livelihood, and safeguarding the environment.








Thanks for sharing the information!